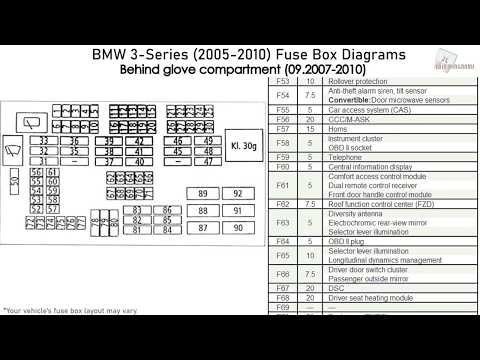
Here you can find info about the 2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box Diagram, pointers, and regularly asked questions. We have actually made this page for people browsing for a 2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box Diagram.
A wiring diagram will show you where the cables ought to be linked, so you do not have to presume.
You don’t have to think, a wiring diagram will show you exactly how to connect the wires.
2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box Diagram
See the 2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box Diagram images below


Tips and techniques for reading wiring diagrams
- Put a blank sheet of paper next to the wiring diagram and just draw the simple circuit. All complex wiring diagrams are simply a series of simple diagrams, and it makes it difficult to look at if you don’t narrow down to the circuit that you’re doing.
- Print the wiring diagram off and utilize highlighters to trace the circuit. When you utilize your finger or follow the circuit with your eyes, it’s easy to mistrace the circuit. One technique that I utilize is to print the very same wiring diagram off two times.
- To correctly check out a wiring diagram, one needs to know how the elements in the system operate. If a module is powered up and it sends out a signal of half the voltage and the professional does not know this, he would think he has a issue, as he would anticipate a 12V signal. Following diagrams is relatively simple, but using it within the scope of how the system operates is a different matter. My finest recommendations is not just look at the diagram, but understand how the elements operate when in use.
- Check out wiring diagrams from negative to positive and redraw the circuit as a straight line. All circuits are the same– voltage, ground, single element, and switches.
- Prior to checking out a schematic, get familiar and comprehend all the symbols. Read the schematic like a roadmap. I print the schematic and highlight the circuit I’m diagnosing to ensure I’m staying on the best course.
2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box | Fuse Box And Wiring Diagram

FAQ
Wiring diagram types
- Schematic Diagrams.
- Wiring diagrams.
- Block diagrams.
- Pictorial diagrams.
Where is a wiring diagram used?
Wiring diagrams are primarily used when attempting to show the connection system in a circuit. It is majorly utilized by building organizers, architects, and electricians to provide the wiring connections in a structure, a room, and even a simple gadget.
Why is wiring diagram crucial?
It reveals the components of the circuit as streamlined shapes, and how to make the connections in between the devices. A wiring diagram normally provides more info about the relative position and arrangement of devices and terminals on the devices.
Why do we need wiring diagrams?
A wiring diagram is often used to troubleshoot problems and to ensure that all the connections have actually been made and that everything is present.
What is the difference in between a schematic and wiring diagram?
A wiring diagram is a generalized pictorial representation of an electrical circuit. The components are represented utilizing streamlined shapes in wiring diagrams.
2006 Bmw 325i Starter Fuse Location – Thxsiempre
2006 Bmw 325i Fuse Box Under Hood – Thxsiempre
2006 Bmw 325I Fuse Box | Fuse Box And Wiring Diagram
Are all wiring diagrams the same?
Wiring diagrams may follow various requirements depending on the country they are going to be used. They may have various layouts depending on the company and the designer who is creating that. They likewise may be drawn by various ECAD software application such as EPLAN or AutoCAD electrical.
What is an architectural wiring diagram?
Architectural wiring diagrams reveal the approximate places and interconnections of receptacles, lighting, and permanent electrical services in a building.
How are wiring diagrams read?
The electrical schematics read from left to right, or from top to bottom. This is important to get right, as the signal direction suggests the flow of current in the circuit. It is then simple for a user to understand when there is a change in the course of the circuit.
How do you check out electrical wire numbers?
An electrical cable is categorized by two numbers separated by a hyphen, such as 14-2. The very first number denotes the conductor’s gauge; the second represents the variety of conductors inside the cable. 14-2 has two 14-gauge conductors: a hot and a neutral.
How do you read vehicle wiring diagrams?
An auto wiring diagram is a map. To read it, recognize the circuit in question and beginning at its source of power, follow it to the ground. Utilize the legend to comprehend what each symbol on the circuit implies.
How do you read wire size charts?
Wire gauges range from low numbers to high numbers, with smaller numbers referring to smaller diameters and bigger numbers representing larger sizes. AWG 4 is 0.2043 inches in size, and AWG 40 is. 0031 inches in size.
How is wire numbered?
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is the standard way to signify wire size in North America. In AWG, the larger the number, the smaller the wire diameter and density. The largest basic size is 0000 AWG, and 40 AWG is the smallest standard size.
What is the schematic format?
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a representation of the aspects of a system utilizing abstract, graphic symbols instead of realistic images.
What should a schematic consist of?
Schematics should consist of the complete description and places of all constructing code components, such as the heating/ventilation/air conditioning (also called HVAC), pipes, and electrical systems. Schematic styles are just a standard design to interact a style scheme to the owner.
Is AWG aluminum or copper?
The AWG requirement includes copper, aluminum and other wire products. Normal household copper wiring is AWG number 12 or 14. Telephone wire is normally 22, 24, or 26. The greater the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire.
Can you touch a live black wire?
If you are available in contact with a stimulated black wire– and you are likewise in contact with the neutral white wire– current will pass through your body. You will receive an electrical shock. You will get a shock if you touch 2 wires at different voltages at the same time.